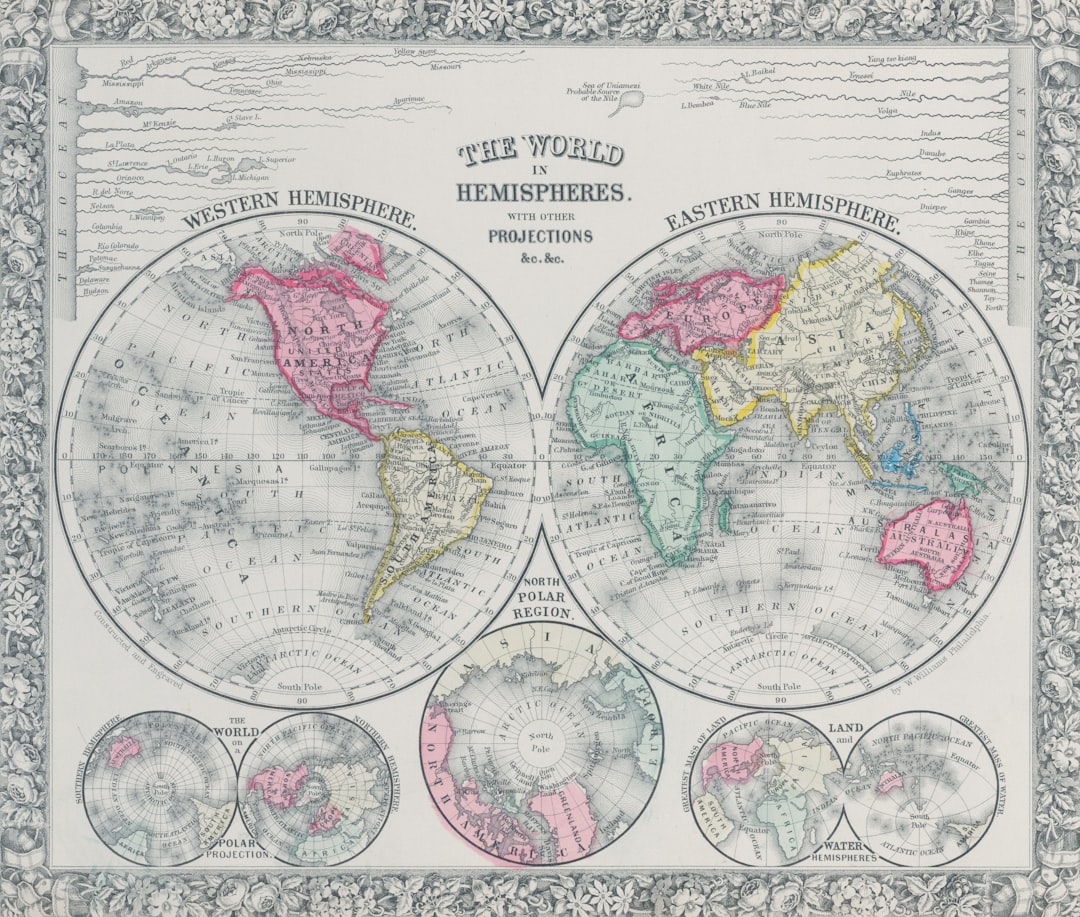
Piri Reis, a name that resonates through the annals of cartography, represents a pivotal figure in the history of map-making during the Ottoman Empire. Born in the late 15th century, he emerged as a prominent navigator and cartographer whose works would leave an indelible mark on the understanding of geography in his time. Ottoman cartography, characterized by its unique blend of artistic expression and scientific inquiry, flourished during this period, with Piri Reis at the forefront.
His maps not only served practical navigational purposes but also reflected the cultural and intellectual currents of the Ottoman Empire, showcasing a synthesis of knowledge from various civilizations. The significance of Piri Reis extends beyond his individual contributions; he embodies the spirit of an era when exploration and discovery were reshaping the world. The maps he created were not mere representations of land and sea; they were intricate tapestries woven from the threads of history, culture, and science.
As Europe began to expand its horizons, seeking new trade routes and territories, Piri Reis’s work provided crucial insights into uncharted waters and distant lands. His legacy is a testament to the rich tradition of Ottoman cartography, which played a vital role in the broader narrative of global exploration.
Key Takeaways
- Piri Reis was an important figure in Ottoman cartography, known for his world maps and contributions to the understanding of the New World.
- Piri Reis’s maps were a result of his extensive knowledge of navigation, geography, and cartography, making him a key figure in the history of mapmaking.
- Ottoman cartography played a crucial role in mapping the world, providing valuable information for exploration and navigation during the Age of Discovery.
- Piri Reis’s world map is considered a masterpiece of Ottoman cartography, showcasing his skill and innovation in mapmaking.
- Piri Reis’s maps had a significant influence on exploration and navigation, contributing to the understanding of the geography of the New World and leaving a lasting legacy in modern geography.
Piri Reis: The Man Behind the Maps
Piri Reis was born in 1465 in Gallipoli, a coastal town in modern-day Turkey. His early life was steeped in maritime culture, as he was the grandson of a famous sailor and navigator. This familial connection to the sea undoubtedly influenced his career choices, leading him to become a naval officer in the Ottoman fleet.
His experiences at sea provided him with firsthand knowledge of navigation and geography, which he would later translate into his cartographic works. Piri Reis’s life was marked by a deep curiosity about the world around him, driving him to explore not only the Mediterranean but also the newly discovered lands across the Atlantic. His most famous work, the “Book of Navigation,” compiled in 1513, is a reflection of his extensive travels and studies.
This book contained maps and navigational instructions that drew from various sources, including ancient texts and firsthand accounts from explorers. Piri Reis’s ability to synthesize this information into coherent maps demonstrated his exceptional skill as a cartographer. His work was not just about creating maps; it was about understanding the world in a holistic manner, integrating knowledge from diverse cultures and traditions.
This approach set him apart from many of his contemporaries and established him as a leading figure in Ottoman cartography.
The Importance of Ottoman Cartography in Mapping the World

Ottoman cartography played a crucial role in shaping the understanding of geography during a time when European powers were expanding their empires and exploring new territories. The Ottomans, with their vast empire stretching across three continents, possessed a wealth of geographical knowledge that was essential for navigation and trade. Their maps were not only tools for sailors but also reflections of political power and cultural identity.
The Ottomans recognized that accurate maps were vital for maintaining control over their territories and facilitating trade routes. The significance of Ottoman cartography lies in its ability to bridge different cultures and knowledge systems. While European cartographers were often focused on their own continent, Ottoman maps incorporated information from Africa, Asia, and Europe, creating a more comprehensive view of the world.
This inclusivity allowed for a richer understanding of global geography, as Ottoman cartographers like Piri Reis drew upon diverse sources, including Arabic, Persian, and even Chinese texts. The result was a body of work that not only served practical purposes but also fostered cross-cultural exchanges and collaborations.
Piri Reis’s World Map: A Masterpiece of Ottoman Cartography
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Title | Piri Reis’s World Map: A Masterpiece of Ottoman Cartography |
| Creator | Piri Reis, an Ottoman admiral and cartographer |
| Creation Date | Drawn in 1513-1514 |
| Medium | Parchment |
| Significance | One of the oldest surviving maps to show the Americas |
| Features | Detailed coastlines, islands, and geographical features |
| Accuracy | Varies across different regions, but generally impressive for its time |
Piri Reis’s world map, created in 1513, stands as one of the most remarkable achievements in Ottoman cartography. This map is notable for its detailed representation of the known world at the time, including parts of Europe, Africa, and South America. What sets this map apart is its artistic quality; it is adorned with vibrant colors and intricate illustrations that bring the geographical features to life.
The map is not merely a functional tool; it is a work of art that reflects Piri Reis’s deep appreciation for beauty and detail. One of the most striking aspects of Piri Reis’s world map is its depiction of the New World. At a time when European knowledge of these lands was still limited, Piri Reis managed to incorporate information from various explorers who had ventured into these territories.
His map includes representations of South America’s coastline and even hints at the presence of Antarctica, showcasing his remarkable foresight and understanding of geography. This blend of artistic flair and scientific accuracy makes Piri Reis’s world map a true masterpiece that continues to captivate historians and cartographers alike.
The Influence of Piri Reis’s Maps on Exploration and Navigation
Piri Reis’s maps had a profound impact on exploration and navigation during the Age of Discovery. As European powers sought new trade routes and territories, they relied heavily on accurate maps to guide their voyages. Piri Reis’s work provided invaluable insights into uncharted waters, helping navigators avoid treacherous areas while identifying potential routes for trade and exploration.
His maps were widely circulated among sailors and explorers, becoming essential tools for those venturing into unknown territories. The influence of Piri Reis extended beyond his immediate contemporaries; his maps inspired future generations of cartographers and explorers. The accuracy and detail found in his works set a standard for map-making that would be emulated by others in both the Ottoman Empire and Europe.
As explorers like Ferdinand Magellan embarked on their journeys around the globe, they carried with them the knowledge gleaned from Piri Reis’s maps, further solidifying his legacy as a key figure in the history of navigation.
Piri Reis’s Contribution to Understanding the Geography of the New World
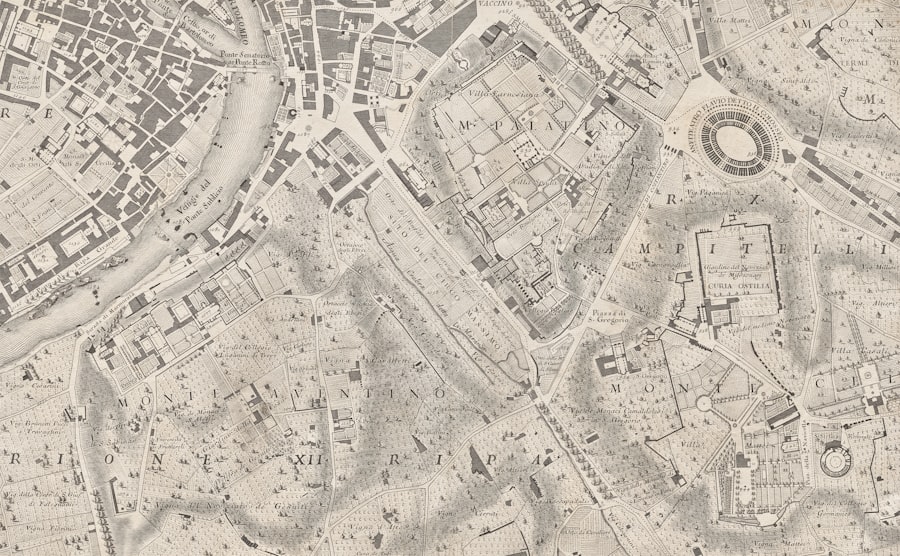
Piri Reis’s contributions to understanding the geography of the New World are particularly noteworthy given the limited information available at the time. His maps provided one of the earliest European depictions of South America, showcasing its coastline with remarkable accuracy. This was no small feat considering that many European cartographers were still grappling with misconceptions about these newly discovered lands.
Piri Reis’s ability to synthesize information from various sources allowed him to create maps that were not only informative but also groundbreaking. Moreover, Piri Reis’s work highlighted the interconnectedness of different regions across the globe. By incorporating knowledge from indigenous peoples and other explorers who had ventured into these territories, he painted a more comprehensive picture of the New World than many of his contemporaries could offer.
His maps served as a bridge between cultures, facilitating an understanding that transcended geographical boundaries. This contribution was instrumental in shaping European perceptions of the Americas and laid the groundwork for future exploration.
The Legacy of Piri Reis and Ottoman Cartography in Modern Geography
The legacy of Piri Reis extends far beyond his lifetime; it continues to resonate within modern geography and cartography. His innovative approach to map-making has influenced countless generations of cartographers who have sought to emulate his blend of artistic expression and scientific rigor. The principles he employed—such as incorporating diverse sources and emphasizing accuracy—remain foundational in contemporary cartographic practices.
Furthermore, Piri Reis’s work serves as a reminder of the rich tradition of Ottoman cartography that has often been overshadowed by European narratives.
In an increasingly globalized world, recognizing figures like Piri Reis allows for a more nuanced appreciation of how different cultures have contributed to our collective knowledge about the planet.
Piri Reis’s Use of Technology and Innovation in Cartography
Piri Reis was not only an exceptional cartographer but also an innovator who embraced technology to enhance his work. During his time, advancements in navigational tools such as compasses and astrolabes were revolutionizing maritime exploration. Piri Reis adeptly utilized these technologies to improve the accuracy of his maps, ensuring that they reflected real-world conditions as closely as possible.
In addition to traditional navigational tools, Piri Reis also incorporated information from various sources into his maps, including ancient texts and firsthand accounts from explorers who had traveled to distant lands. This innovative approach allowed him to create maps that were not only visually stunning but also rich in detail and context. By blending technology with diverse knowledge systems, Piri Reis set a precedent for future cartographers who would continue to push the boundaries of map-making.
The Historical and Cultural Context of Piri Reis’s Cartography
Understanding Piri Reis’s work requires an appreciation for the historical and cultural context in which he operated. The early 16th century was marked by significant geopolitical changes as European powers expanded their empires through exploration and colonization. The Ottoman Empire itself was at its zenith during this period, exerting influence over vast territories across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
In this environment, cartography became not just a practical tool but also a means of asserting power and identity. For Piri Reis, creating maps was an act that transcended mere navigation; it was a way to document and celebrate the richness of diverse cultures within the empire. His work reflects a deep engagement with both local knowledge systems and global currents, showcasing how geography can serve as a canvas for cultural expression.
Piri Reis’s Impact on the Development of Cartography in the Ottoman Empire
Piri Reis’s impact on cartography within the Ottoman Empire cannot be overstated. He established a standard for map-making that emphasized accuracy, detail, and artistic quality—principles that would influence subsequent generations of Ottoman cartographers. His innovative techniques paved the way for others to explore new frontiers in map-making while maintaining a commitment to cultural inclusivity.
Moreover, Piri Reis’s work fostered an environment where knowledge could be shared across cultures. By drawing upon diverse sources—from ancient texts to contemporary explorers—he created maps that reflected a rich tapestry of human experience. This collaborative spirit became a hallmark of Ottoman cartography, encouraging future cartographers to engage with various cultures as they sought to document an ever-changing world.
Piri Reis’s Enduring Legacy in the World of Cartography
Piri Reis’s enduring legacy in the world of cartography is a testament to his exceptional skill as both a navigator and an artist. His maps not only provided practical guidance for explorers but also served as cultural artifacts that captured the spirit of an era marked by discovery and innovation. Through his work, Piri Reis bridged gaps between different cultures while advancing the field of cartography itself.
As modern geographers continue to explore new frontiers in mapping technology and techniques, they can draw inspiration from Piri Reis’s commitment to accuracy, creativity, and cultural inclusivity. His contributions remind us that cartography is not merely about representing physical spaces; it is also about understanding our place within a complex web of human experiences across time and space. In this way, Piri Reis remains an enduring figure whose influence continues to shape our understanding of geography today.
Piri Reis, an eminent figure in Ottoman cartography, is renowned for his detailed and advanced maps, which have intrigued historians and geographers alike. His most famous work, the Piri Reis map, created in 1513, showcases the remarkable geographical knowledge of the time, including parts of the Americas. For those interested in exploring more about the historical context and significance of Piri Reis’s contributions, a related article can be found on the Real Lore and Order website. This article delves into the intricacies of Ottoman cartography and the legacy of Piri Reis. You can read more about it by visiting this page.
WATCH THIS 🧊The US Military Confirmed It: What’s REALLY Under the Antarctic Ice?
FAQs
What is Ottoman cartography?
Ottoman cartography refers to the map-making tradition of the Ottoman Empire, which was known for its detailed and accurate maps of the regions under its control. Ottoman cartographers were skilled in creating maps that depicted not only geographical features, but also political boundaries, cultural landmarks, and trade routes.
Who was Piri Reis?
Piri Reis was an Ottoman admiral, geographer, and cartographer who lived in the 16th century. He is best known for his world map, the Piri Reis map, which is one of the oldest surviving maps to show the New World and is considered a significant achievement in the history of cartography.
What is the Piri Reis map?
The Piri Reis map is a world map created by Piri Reis in 1513. It is drawn on a parchment and depicts the coastlines of Europe, Africa, and the Americas. The map is notable for its accurate representation of the coast of Brazil and its inclusion of the Antarctic coastline, which was not officially discovered until centuries later.
What makes the Piri Reis map significant?
The Piri Reis map is significant because it provides evidence that ancient seafarers had knowledge of advanced cartography and may have had access to sources of information that are now lost to history. The map has also sparked debate and speculation about the possibility of pre-Columbian contact between the Old World and the Americas.
What is the current status of the Piri Reis map?
The original Piri Reis map is housed in the Topkapi Palace Museum in Istanbul, Turkey. It has been extensively studied and analyzed by scholars and remains a subject of interest for historians, cartographers, and enthusiasts of ancient maps.